Value investing is an investing strategy commonly used in the stock and futures markets. The strategy is based on the estimation of the “real price” of the share. To estimate this, investors calculated the Fair Value of the Share by considering buildings, machinery, production, financial instruments owned by the company, equity, cash flow, debt, and all interest earned until debts are paid. Dividing the sum of these factors by the number of shares, we get the Fair Value of the Share.
Then, the investors compare the calculated Fair Value of the share against the current price in the stock market. What the investor wants to find is an underrated share. This is that the current stock price is lower than the calculated share price.
Can we apply this to currencies?
The simple answer is no. A currency has no future cash flow, and a nation doesn’t have a total value. Thus, many of the things used to get the Fair Value of a company can’t be estimated in Forex. However, Value Investing uses techniques that are similar to fundamental analysis.
In many ways, the pair Company-Share is similar to Nation-Currency. The currency value is affected by the economy of the state, this is not always directly related, but most of the time it is.
In this way, considering the differences between both markets, we can say that there is a type of analysis similar to Value Investing in Forex.
The analysis is also based on the currency’s Fair Value, and what the investor should look for when analyzing the currency, is the economic shape of the nation. The analysis should include GDP, inflation, political developments, economic sectors, internal and external debt, and similar elements.
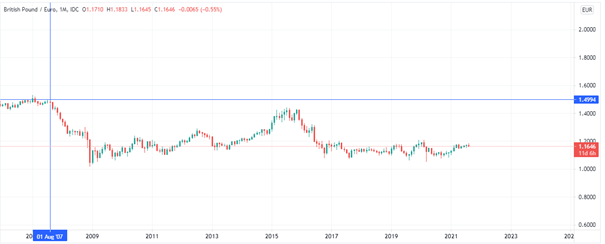
Above, we can see the change in the price of the pair GBP/EUR since the 2008 crisis. Since then, the UK has outperformed the EU’s economy, and even political events like Brexit haven’t changed the trend.
How to apply the strategy?
While stocks are valued in terms of currencies, currencies are measured against other currencies. So, while an investor in the stock markets looks for underrated shares, in Forex you want to find a pair in which one of the currencies is underrated in comparison to the other. In this way, you need to study two instead of one currency.
The simplest way to effectively compare two currencies is through Purchasing Power Parities. The PPP are rates of currency conversion that try to equalize the purchasing power of different countries. Once you get the PPP of the two currencies you plan to trade, you should look at the current valuation of the pair in the market. If you find that one of the currencies is underrated against the other, you want to buy the underrated currency and sell the overrated.
There are other quantitative and qualitative ways of doing the analysis. There is the Big Mac index which compares the price of the famous burger among countries. Also, the most used qualitative technique is to compare the economic shape of the nations and decide which one is stronger now and in the future.
Bottom line
Strictly speaking, you can’t value investing in Forex. But, some fundamental analysis techniques are very similar to value investing. The principle of the strategy is that the market value will always tend to equalize the Fair Value of the asset. What the investors want is to find an underrated currency and wait until its value rises to meet the Intrinsic Value.
This is actually the essence of trading. The main difference between trading and investing is that investors look for profits in the long term while traders take advantage of the market volatility in the short term.

